Table of Contents
Welcome to our comprehensive cannabis concentrates guide. The legalization of marijuana in Canada has seen a dramatic increase in the popularity and demand for concentrates.
Concentrates are an excellent option for cannabis enthusiasts looking to enhance the intensity of their high. They are also great for flavour connoisseurs looking to experience the most exquisite terpene profiles.
For medical marijuana patients, concentrates offer a direct, more economical, faster-acting solution to their health issues. Read on to learn more about cannabis concentrates.
What are Cannabis Concentrates?
Cannabis concentrates are cannabis-derived extracts containing concentrated amounts of the psychoactive compound THC and several other cannabinoids and terpenes. There are many different types of concentrates divided into two primary categories.
- Solvent extractions
- Solventless extractions
You’ll learn more about these when we look at the types of cannabis concentrates. Concentrates are more potent than regular marijuana. They are ideal for those looking for a more intense effect.
They are also an excellent option for those looking for efficiency with their cannabis consumption because a little concentration can go a long way.
Types of Concentrates
Concentrates represent a wide range of different products. We recognize these products based on their extraction method and the part of the plant used for extraction. There are two main types of concentrates: solvent-based and non-solvent concentrates.
A solvent is a substance that dissolves another substance to produce a liquid solution. Solvents used in extracting solvent-based concentrates include propane, butane, alcohol, and carbon dioxide (CO2). These solvents help to separate resin glands that contain cannabinoids from the cannabis flower.
In non-solvent extractions, temperature, pressure, and water are the predominant factors. These types of extractions don’t introduce foreign substances, except water. They are arguably the best quality and most unadulterated form of cannabis extracts.
Furthermore, you can easily perform non-solvent extraction techniques at home. These reasons make non-solvent extractions the most preferred cannabis concentrates. That said, let’s explore some of the common types of concentrates on the market:
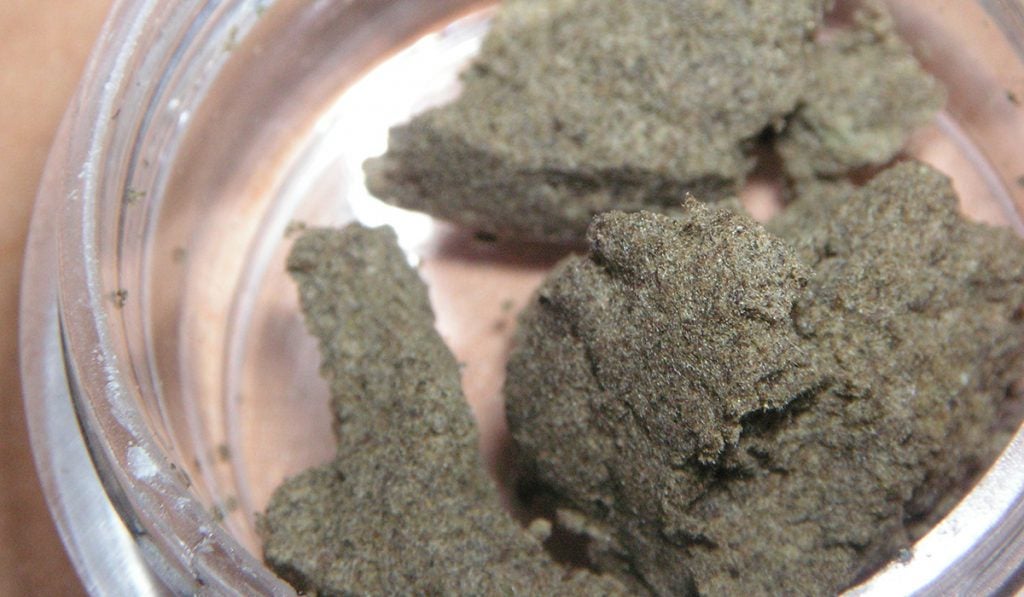
Hash
Hash is perhaps the oldest marijuana concentrate in human history. Making hash involves condensing kief and oils from the cannabis plant to form a tight, dense substance.
Hash is the only processed concentrate you can make without chemical solvents or sophisticated technology. It has a dark brown appearance and is of three types:
- Finger hash
- Grinder hash
- Bubble hash
Finger hash is the oldest type of hash. It is still prevalent in the Caribbean islands and India. You can obtain it by vigorously rubbing plant material between your hands until you get a sufficient layer of kief and oils that you can scrape off.
You can also make hash by dropping some bud and plant material into ultracold ice water. This shocks the trichomes, causing them to fall off the plant. You can then filter the trichomes out of the water and dry them out. What you get in the end is bubble hash.
Also Read: How to Smoke Hash in a Bong
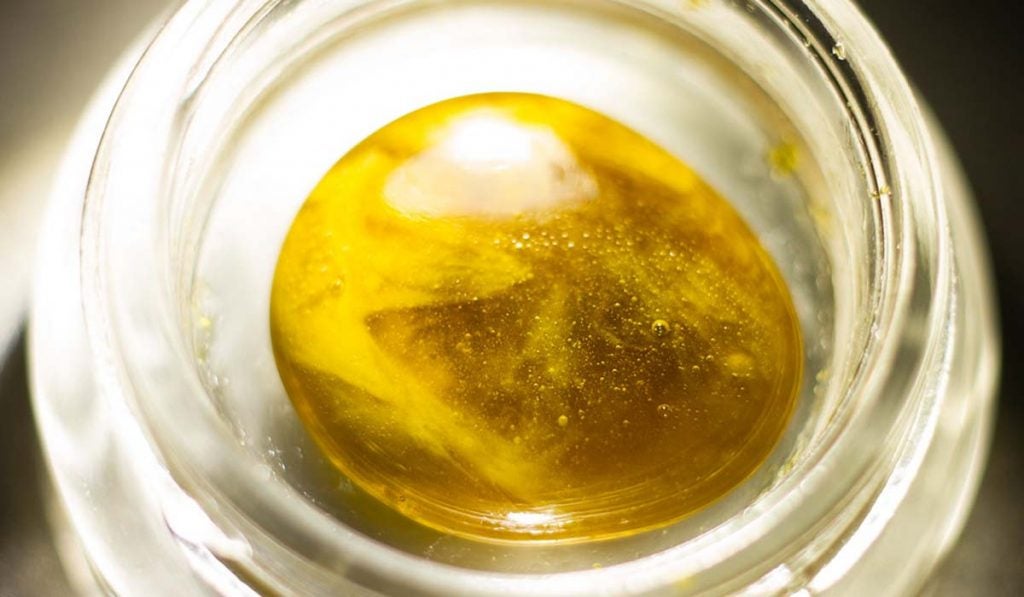
Shatter
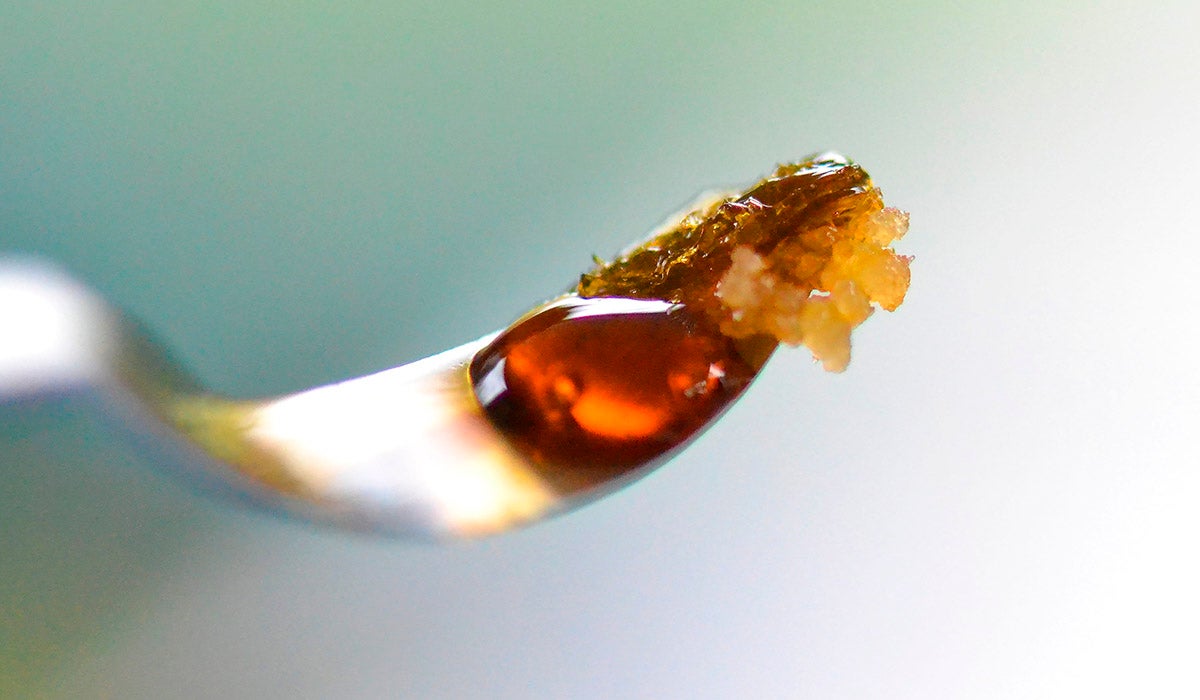
Shatter is among the purest cannabis concentrates you can find. Making it involves using a solvent to extract THC from cannabis flowers. The process is known as the butane hash oil extraction.
It is not safe to perform this kind of extraction at home. That’s because the solvent has to be removed completely from concentrate for it to be safe for human consumption.
Shatter resembles a coloured piece of glass with a candy-like consistency. It is exceptionally powerful, with at least 80% THC. However, it is slightly deficient in flavor. There are different ways to use shatter, including dabbing and vaping.
Distillate
Distillate is one of the newest types of cannabis concentrates on the market. Its production involves using highly scientific equipment to heat and vaporize the cannabinoids within the cannabis flower. Then, you pass the vapour into a cooling system for consolidation and collection into beakers.
Residual solvents, chlorophyll, and other by-products remain behind after collecting the cannabinoid-rich vapor. The process is called short path distillation. It removes most, if not all, of the terpenes in the cannabis plant.
The temperatures are so high that terpenes may not survive the process. You can repeat the distillation several times to create the purest of distillates possible.
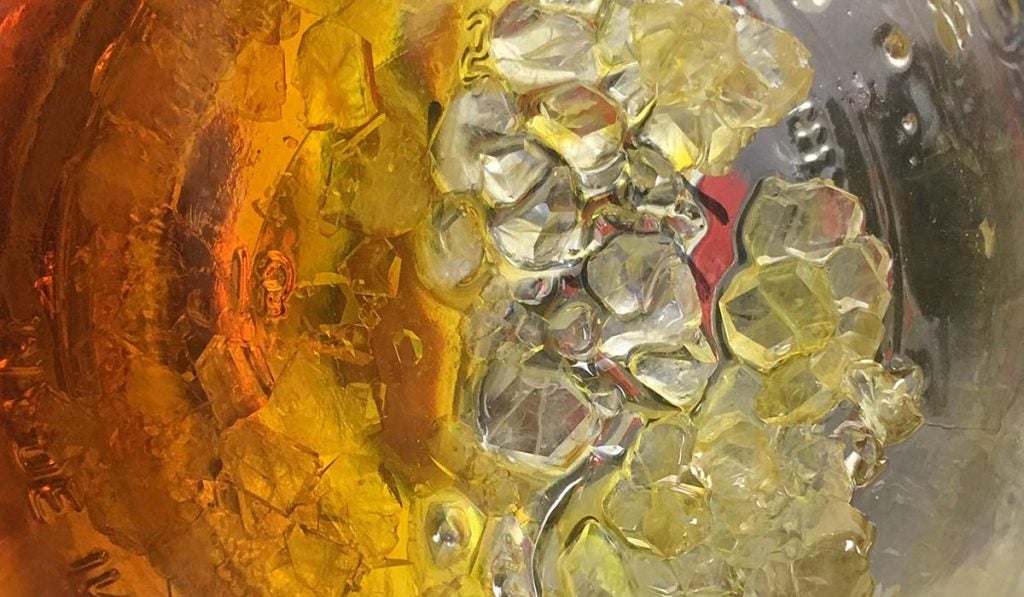
HTFSE, HCFSE, Diamonds
High terpene full spectrum extract (HTFSE) and high cannabinoid full spectrum extract (HCFSE) diamonds are cannabis extractions produced with a mixed hydrocarbon solvent: isobutane/propane/N-butane.
The extraction process involves pulling out the valuable therapeutic molecules from the cannabis plant, leaving the non-therapeutic molecules like waxes, lipids, and fats behind. For HTFSE, the process focuses on achieving a full terpene profile.
HCFSE, on the other hand, focuses on preserving a full range of cannabinoids. This extraction takes on a diamond-like consistency, usually referred to as HCFSE diamonds. HTFSE, on the other hand, assumes an oil or sauce-like texture.
The extraction has THCA crystals suspended in the sauce. Industry experts refer to HTFSE as “The Sauce” or “Terp Sauce.” Unlike other concentrates, the extraction of HTFSE requires highly specialized equipment. Therefore, you cannot perform its extraction at home.
HTFSE and HCFSE extractions not only boast a better flavor and aroma profile, but they also have enhanced therapeutic value. That’s because the full spectrum of compounds from the plant material makes it to the final product.
THC-A & CBD Crystallite
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THC-A) and Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) are the two most dominant cannabinoids present in the cannabis plants’ trichomes. They are unstable precursors to their pharmacologically active compounds, THC and CBD.
As the living cannabis plant undergoes the final stages of senescence, THC-A and CBDA decarboxylate gradually become active. After harvesting and drying the plant, you can use various forms of heat to decarboxylate the cannabinoids into their active compounds.
Isolated THC-A and CBD are the purest forms of cannabis concentrate you can find. Their potency can go up to 99.9%. That means they have nothing else from the original plant, including terpenes, lipids, fats, and flavonoids.
That explains why THC-A and CBD isolates have little or no flavor, aroma, and color. THC-A and CBD molecules take on a crystalline shape with rigid and latticed structures.
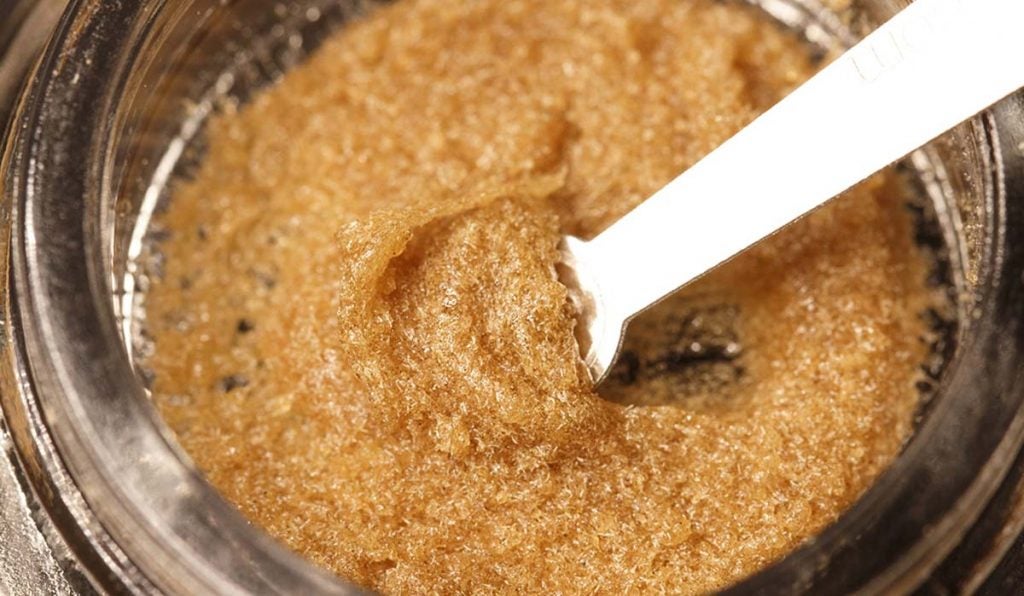
Rosin vs. Live Resin
Rosin and live resin are among the many types of cannabis concentrates available on the market today. While they have similar names, the two products differ significantly.
Live resin refers to a solvent-based concentrate derived from live or freshly frozen cannabis plants. The solvent helps to extract the resin glands before they dry and cure, which preserves the plant materials’ terpene profile.
Conversely, rosin is a non-solvent concentrate usually created by pressing bubble hash. This process preserves the plant’s live terpene profile without using solvents. Bubble hash serves as a water sieve rather than an extraction solvent.
While high-quality rosin is usually a result of specialized equipment, there are various easy ways to make it at home. For live resin, the extraction process is quite complicated. The complexity makes live resin rare and expensive, and some users tend to confuse rosin for live resin.
Oils
Oils are another type of cannabis concentrate. There are several different types of cannabis oils, including the following:
THC Oil
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is one of the primary components of cannabis. THC oil is an oil derived from THC-rich cannabis flowers. There are several different ways of making THC oil, and manufacturers can infuse it in various types of carrier oils. You can also make or buy a full spectrum of THC oils.
If you’re looking for the best honey oil in Canada, be sure to check out our blog! We’ll show you where to find the highest quality products and how to use them.
CBD Oil
Cannabidiol (CBD oil) is among the most popular cannabis oils. There are different methods to make CBD oil, including carbon dioxide extraction and ethanol-based extraction techniques. Manufacturers make it using CBD-rich strains or hemp plant flowers.
Butane Honey Oil (BHO)
BHO is a concentrate of the aromatic and active compounds of the cannabis plant. As the name suggests, its production involves using liquid butane as a solvent.
BHO samples usually have high levels of cannabinoids, with THC concentrations ranging from 70 to 90%. You can use BHO by dabbing or vaporizing.
Phoenix Tears/RSO
Phoenix Tears (Rick Simpson Oil) is a cannabinoid extract made with any solvent apart from butane. Many manufacturers use food-grade alcohol like pure ethanol because it is much less toxic. You can use RSO directly by oral or sublingual administration. A similar product is FECO (Full Extract Cannabis Oil), made with grain alcohol.
Tinctures
Tinctures are alcohol-based cannabis extractions. While manufacturers often use alcohol to make them, you can also use glycerin to avoid the intoxicating effects of alcohol.
The alcohol serves as a solvent to extract cannabinoids and terpenes from the rest of the plant material. Tinctures are edibles. Hence, it is vital to decarboxylate the cannabis used.
You want to ensure all the components are active. Otherwise, the tincture won’t be as effective as expected. Tinctures are a great option for first-time cannabis users for the following reasons:
- They are discreet. You can easily conceal them in a small container in your bag.
- Effects from cannabis tinctures set in faster compared to other cannabis products like edibles.
- Tinctures are easy to dose. With a tincture, you can easily find your preferred dosage.








Recent Comments